-
 Toll Free No 9146-744-744
Toll Free No 9146-744-744 - Appointment
A procedure that creates more space inside an artery which has built up plaque inside its lumen is called Angioplasty. A balloon is used to stretch open a narrowed or blocked artery then stent is placed in its lumen to let go of blood flow easily. It restores blood flow to the heart muscle without open-heart surgery. Angioplasty can be done in an emergency setting such as a heart attack or it can be done as elective surgery if your doctor strongly suspects you have heart disease. Angioplasty is called Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI).
Individuals who are diagnosed with coronary artery disease or a heart attack may need to go through coronary angioplasty. Angioplasty can also be performed on other parts of the body that have narrowed or blocked arteries like in the neck, arms, legs, kidneys, and pelvis. The procedure allows blood to flow easily through the arteries that have been narrowed or blocked with plaque.
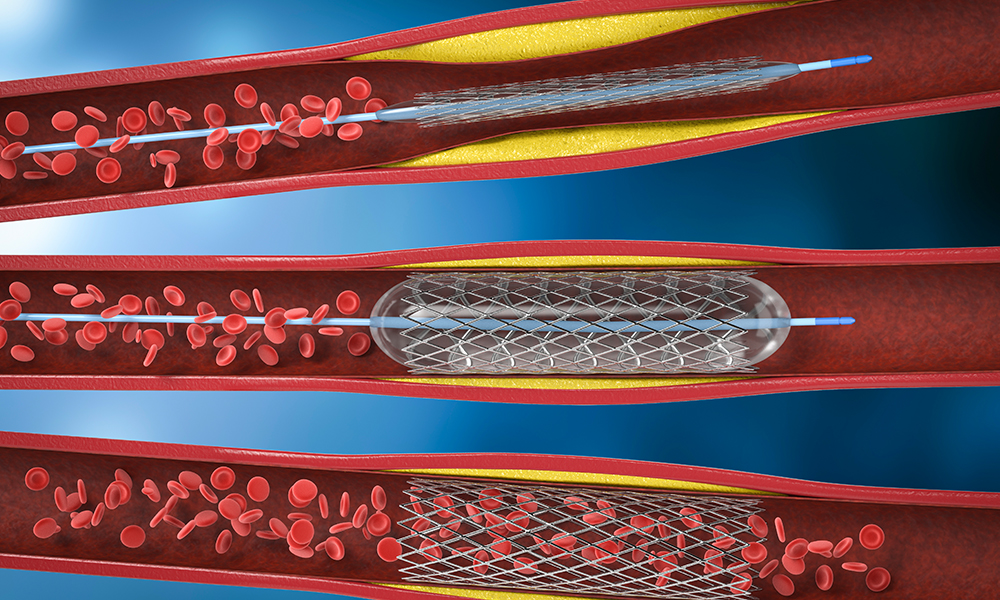
A thin plastic tube called a sheath is inserted into an artery in arm. A catheter passes through the sheath and dye is injected through the catheter. Using images doctors put in a wire and catheter that has a small balloon at the end. The balloon is inflated in the artery which moves the plague out of the way and allows the blood to flow easily through the artery. A strong metal stent is put in the artery that keeps the artery open after the removal of the balloon.
A catheter with a small balloon tip is guided to the narrowed or blocked artery. Once placed, the balloon is inflated to push the plaque and stretch the artery to open boosting the blood flow to normal.
A small metal scaffold is placed inside the artery to let it open. Over several weeks, the artery heals around the stent.
A special catheter, with corn-shaped, diamond-coated is guided to the point of a narrowing artery. The tip then spins at a high speed and grinds away the plaque on artery walls. The particles are washed away in the bloodstream. (This is a rarely used procedure sometimes alongwith Balloon Angioplasty so as to have better results )
A catheter with small blades is inserted in the artery. The blades are activated when the balloon is inflated. The small blades score the plague and then the balloon presses the plaque against the artery wall.
Angioplasty treats Atherosclerosis (a collection of plague and cholesterol in the heart artery or arteries in several parts of the body)
What is it?
It's used as an alternative to CABG. The Shockwave Intravascular Lithotripsy (IVL) consists of a Shockwave C2 catheter, a connector cable, and a generator. The catheter is a tube-like device that contains integrated lithotripsy emitters that can break up hard materials (Calcification) that restricts blood flow to the heart.
The tool enables the opening of calcified arteries so that stents can be placed. Of the 384 patients who participated in the clinical trial, 92% were able to receive the stent and endured 30 days without experiencing a heart attack or undergoing any other surgery. About 75% of patients were still alive after a year without experiencing a heart attack or needing any more procedures.
The cost of Angioplasty is based on:
Possible risks and complications associated with angioplasty, and stenting includes:


Coronary angioplasty is the procedure that removes the blockages from the arteries and allows blood to flow to your heart muscle. It opens the clogged artery by inflating a tiny balloon in it and stent placing in the lumen.
Benefits of angioplasty include:
Restenosis is a problem that can occur after angioplasty. This can cause the artery to become narrow and blocked again often within six months.
After the procedure, the patient is discharged from the hospital within 12 to 24 hours after the catheter is removed. Many patients can return to routine work within a few days to a week.
The success rate of angioplasty is about 60 percent. As the technology improves, the applicability and success rates of angioplasty may improve.
The patient generally can return to their routine work. Before the angioplasty, drink plenty of water to help contrast dye flush out of the body. Avoid rigorous exercise and lifting heavy weights for at least a day after the procedure.
Stents reduce the renarrowing that occurs after the balloon angioplasty. It also helps restore normal blood flow and keep the artery open.
When the patient had coronary angioplasty with no complications such as bleeding or no chest pain, then it is safe to travel or fly 2 days after the procedure.
Some insurance providers cover the daycare procedures. Talk to our HospiOne Team who will guide you with every question you have.
The patient will initially undergo cardiac catheterization. Sedatives will be given to relax. The doctor will then numb the part of the body where the catheter will go.
Then a thin plastic tube called a sheath is inserted into an artery, from the groin, or in your arm. A long narrow hollow tube – a catheter passes through the sheath and is guided towards a blood vessel to the arteries surrounding the heart.
A small amount of contrast liquid or dye is put into the blood vessel through the catheter. It allows doctors to photograph with an X-ray as it moves through your heart’s chambers, valves, and major vessels. The images will let doctors know the exact narrowing or the blockages present in the arteries.
Once the problem area is detected, doctors will then put in a wire and catheter that has a small balloon at the end. The balloon is inflated in the artery which moves the plague out of the way and allows the blood to flow easily through the artery. A strong metal stent is put in the artery that keeps the artery open after the removal of the balloon.
OUR PROCESS IS EASY contact us for More information.
Copyright © 2023 hospione.com - All Rights Reserved | Developed by Digital Marketing StudioGenix LLP